CAR summary data
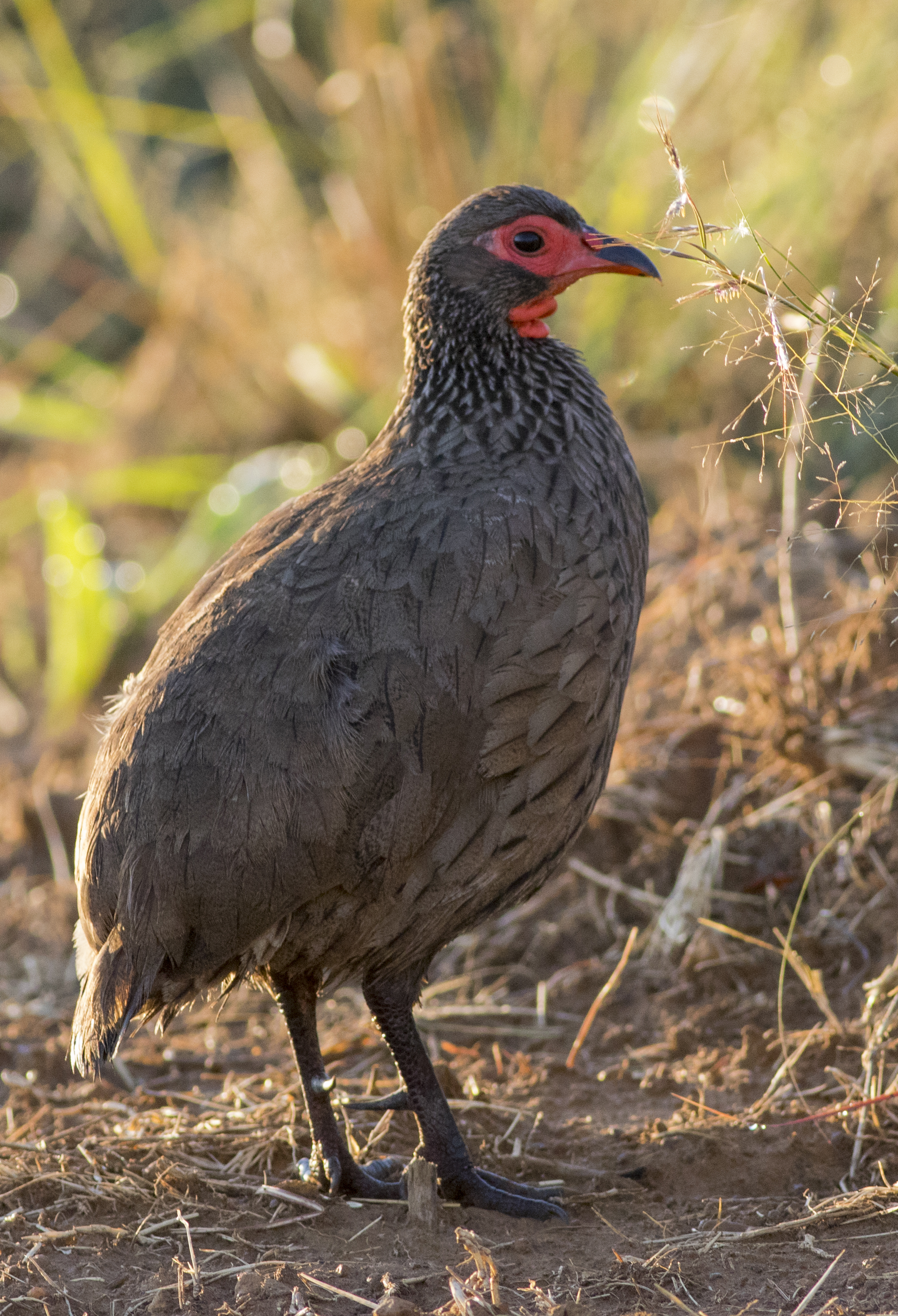
Habitat and noted behaviour
Sightings per Kilometre
Please note: The below charts indicate the sightings of individuals along routes where the species has occured, and NOT across all routes surveyed through the CAR project.
Global Status


IUCN Data (Global)
IUCN 2024. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2024-1
(www)Assessment year: 2024
Assessment Citation
BirdLife International 2024. Pternistis swainsonii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2024: e.T22678860A263600672. Accessed on 03 March 2026.
Taxonomic notes:
Pternistis swainsonii (del Hoyo and Collar 2014) was previously placed in the genus
Francolinus. Original note from Illustrated Checklists: Has been thought to be close to
P. leucoscepus,
P. rufopictus and
P. afer. One genetic study indicated that present species and
P. afer are each other’s closest relatives, although the other two species (
P. leucoscepus,
P. rufopictus) were not sampled (Bloomer and Crowe 1998). Syringeal characteristics partially substantiate this arrangement (Mandiwana-Neudani
et al. 2011). Hybridizes with
P. afer in NE Zimbabwe (near Harare) and with
P. natalensis in SW Zimbabwe (Bulawayo); suspected of hybridizing also with
Ortygornis sephaena in Limpopo Province of N South Africa (Engelbrecht and Grosel 2007). Name
cooperi refers to a hybrid between present species and
P. afer (Irwin 1981). Geographical variation slight, and several additional described subspecies are considered doubtfully valid:
damarensis (Waterberg, in NC Namibia),
gilli (N Namibia to W Zambia and N Botswana) and
chobiensis (NE Botswana to W Mozambique) all included in nominate
swainsonii. Two subspecies recognized.
Population:
The global population size has not been quantified, but the species is reported to be generally common to abundant (del Hoyo et al. 1994, Fuller et al. 2000). The population is suspected to be stable in the absence of evidence for any declines or substantial threats.
Rationale:
This species has an extremely large range, and hence does not approach the thresholds for Vulnerable under the range size criterion (Extent of Occurrence under 20,000 km² combined with a declining or fluctuating range size, habitat extent/quality, or population size and a small number of locations or severe fragmentation). The population size has not been quantified, but it is not believed to approach the thresholds for Vulnerable under the population size criterion (under 10,000 mature individuals with a continuing decline estimated to be over 10% in ten years or three generations, or with a specified population structure). The population trend appears to be stable, and hence the species does not approach the thresholds for Vulnerable under the population trend criterion (over 30% decline over ten years or three generations). For these reasons the species is evaluated as Least Concern.
Trend justification:
The population is suspected to be stable in the absence of evidence for any declines or substantial threats.
Trade use:
This species has been reported as used in trade at a low prevalence, being found in two of the seven trade datasets evaluated (Donald et al. 2024).

 Login
Login



